Logging-Framework: Serilog
Ich werde ab und zu gefragt wie ich denn Daten zur Laufzeit (nicht Debugging) mit logge.
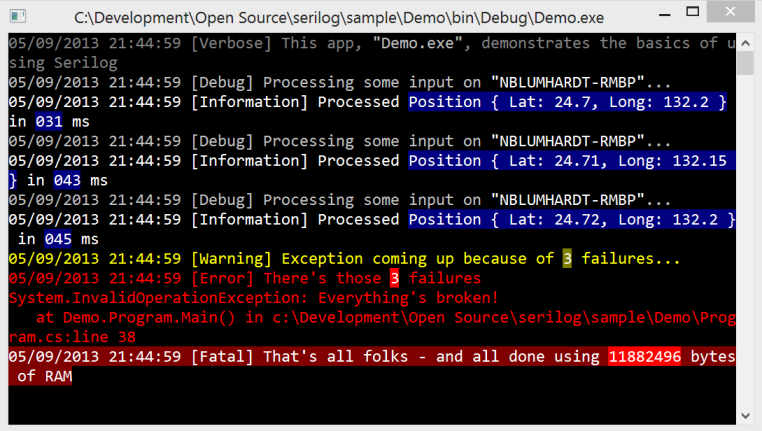
Log4Net war hier lange Platzhirsch, aber für mich und viele andere ist es nun Serilog. Denkbar einfach zu implementieren. Es gibt viele Sinks (Ziele für das Logging, z.B. Datenbanken, Dateien, Console).
Das ganze in kostenlos und OpenSource…
Hier ein kleines Beispiel für einen Logger der in eine Datei schreibt und zusätzlich in die Console, auch schön in Bunt von hier:
Log.Logger = new LoggerConfiguration()
.WriteTo.LiterateConsole()
.WriteTo.RollingFile("log-{Date}.txt")
.CreateLogger();
Log.Information("Ah, there you are!");